Before we begin, you should know that Triads in Music are an excellent and a very useful tool for composing melodies and rhythms! I believe that every musician should equip himself with the grasp of Triads patterns and Triads structure anytime during his musicianship.
Now with that thought, let’s look into different types of Triads, Triad chords and Triad inversions in this text.
Triads definition in music
Basically, Triads-music theory is made up of 3 notes. It can be defined as a three-notes (spaced at intervals of a Third) chord built by arranging Major- Minor- Diminished or an Augmented notes on top of each other.
Check out the article on Chords to understand the concept better.
Remember that these Triad chord progressions are different across Musical Genres starting from classical to contemporary. It’s the different types of Triads that creates swell or a resolution in the songs or instruments that we listen and cherish today.
Triad structure
Triad structure refers to the order of the three notes in them and the Intervals between them. Wondering what an Interval is? In the simplest words, Interval is the distance between any 2 notes you find in music. Essentially, a Triad pattern consists of a Root, Third and a Fifth notes as shown in the image below.
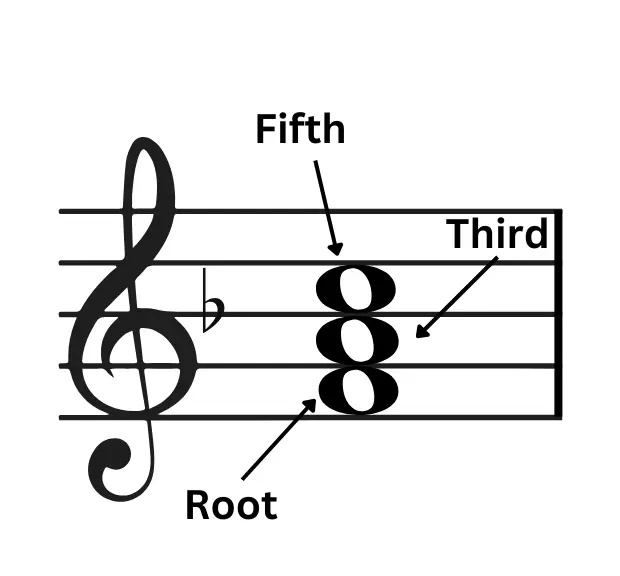
Root
The root can be defined as the foundational note of the Triads in music. It is the first note upon which the Triads Chords are built i.e., other notes measured relatively based on it.
Third
Next on a Triad structure would be the Third, ie, the 2nd note. This note actually decides whether the triad is in Major or Minor.
Fifth
Triad chords’ last note would be the Fifth, which is counted up from the root note. It is this note that determines if the Triad is Augmented or Diminished.
Different types of triads in music
To begin with, there are 4 common yet different Triads in Music. Major and Minor Triads along with Diminished and Augmented Triads. You should know that each type of Triad chord progressions has a distinct sound and characteristics. Not to mention that, they play a different role in music.
Let’s look at the Different types of Triads in Music
Major triads
ROOT + MAJOR THIRD + PERFECT FIFTH
A Major Triad structure looks exactly like the image shown. Let’s break that formula down! A major third is an interval measured from the root note which has 4 semitones or 2 tones. A perfect fifth needs to be counted from the root note and it consists of 7 semitones.
For Instance,
F major Triad in Music, is F ( root note)- A (the Third, 4 semitones from F)- C (the fifth note, 7 semitones from F).

A Major Triad chord has a bright sound. These are often marked with tonic (I), mediant (iii) and dominant (V) in western music.
Minor triads
ROOT + MINOR THIRD + PERFECT FIFTH
A minor Triads in music theory consist of a flattened Third called Minor Third and the rest of the notes as same as a major Triad.
Root note to Minor third (3 semitones) and Root Note to Perfect Fifth(7 semitones).
For example,
The F minor triad is F-Ab-C
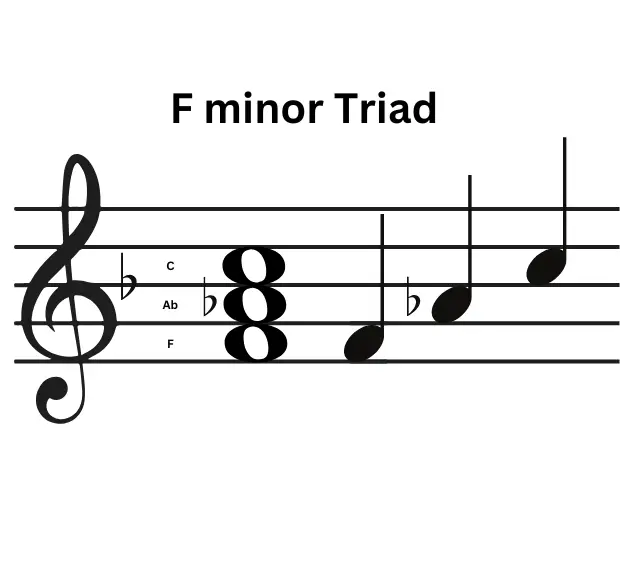
If you look at the F minor triad as shown in the image, the interval between the notes F and Ab is a minor third (3 semitones). The interval between F and C is a Perfect Fifth which adds to 7 semitones. .
Point To Remember!
Minor Triads in music have a gloomy and dull sound.
Augmented triads
ROOT + MAJOR THIRD + AUGMENTED FIFTH
The structure of an Augmented Triad has the same structure of Major and minor Triads but with a little adjustment. It consists of Root, Major Third (4 semitones) and an Augmented Fifth(8 semitones).
For example,
C Augmented Triad pattern is F-A-C#
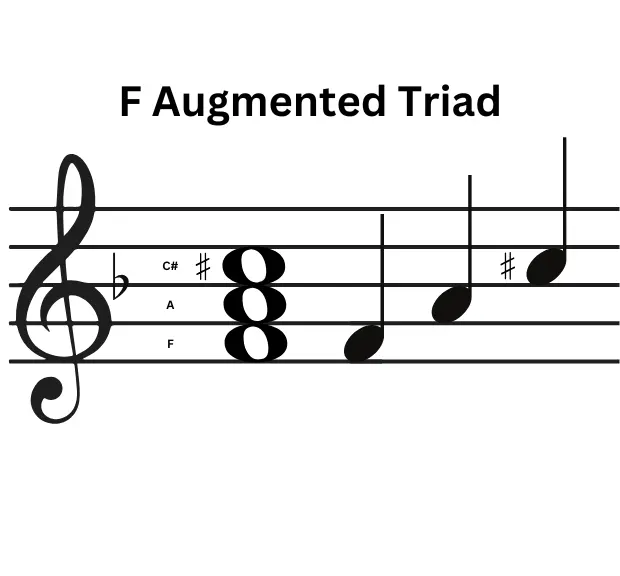
The interval between the notes F and A is Major Third (4 semitones) and the interval F and C# is called Augmented Fifth which exactly is 8 semitones.
Point To Remember!
Minor Triads chord progressions sound quite mysterious, bright yet unstable.
Diminished triads
ROOT + MINOR THIRD + DIMINISHED FIFTH
A Diminished Triad structure consists of Root, Minor Third (3 semitones) and a Diminished Fifth (6 semitones).
For example,
F Diminished Triad pattern, i.e, F-Ab-Cb

F-Ab-Cb is almost the same as an Minor triad except for the flattened fifth note. The interval between the notes F and Ab is Minor Third (3 semitones) and the interval F and Cb is called Diminished Fifth which is exactly 6 semitones.
Point To Remember!
Minor Triads chord progressions sound quite mysterious, bright yet unstable.
Wondering what Augmented or Diminished mean. Checkout this article on Different Types of Intervals in Music to find what Augmented or Diminished means. Now, moving on the concept of Triad Inversions.
Triad inversions
I would say that the concept of Inversions are quite essential in music as they make things easier. Though the word sounds a bit fancy, Triad Inversions are fairly a simple concept.
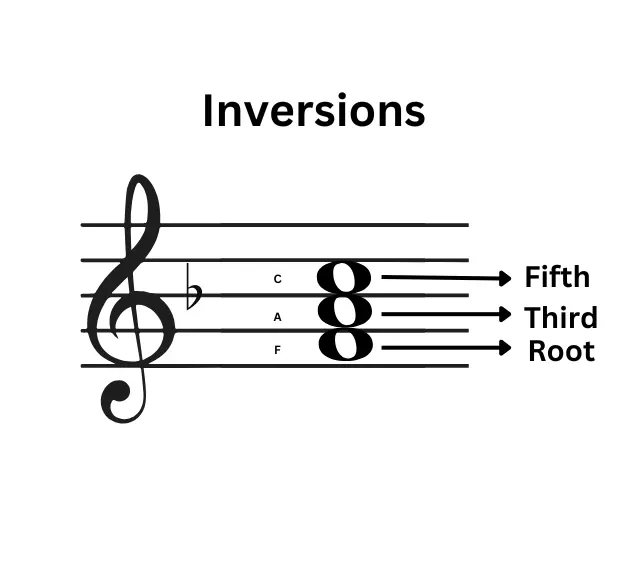
Triad Inversions refers to the rearrangement of the notes of a Triad. Simple, isn’t it? We now know that Triads definition music has 3 notes in it and in the order Root-Third-Fifth. This particular order gives different harmonic flavours. Now changing this order i.e., the positions of the Root, Third or Fifth is the gist of the concept of Inversions.
Let’s look at the types of Triad Inversions
First inversion of triads in music
Just as we’ve learnt so far, in music theory, Triads is a concept consisting of 3 notes written in ROOT + THIRD + FIFTH position. Changing any note would result in a different sound. Now, changing the position of the Third Note to the root position is called the First Inversion of any Triad.
For example,
Let me remind you of the F major Triad Structure, F-A-C.
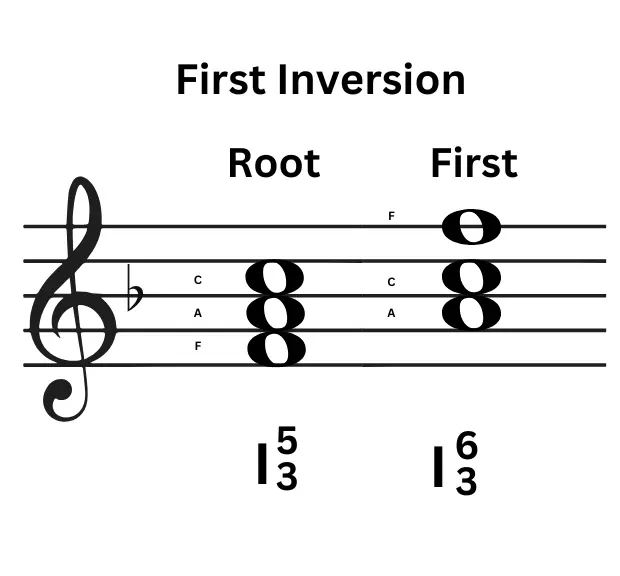
Here the position of A, that is the Third is pulled down to bass and the root note F is changed to the position of C, that is the Fifth. This results in A being the root note, C the Third and F the Fifth.
Point To Remember!
First Inversion Triads tend to have a smoother sound and create a sense of movement between the progressions .
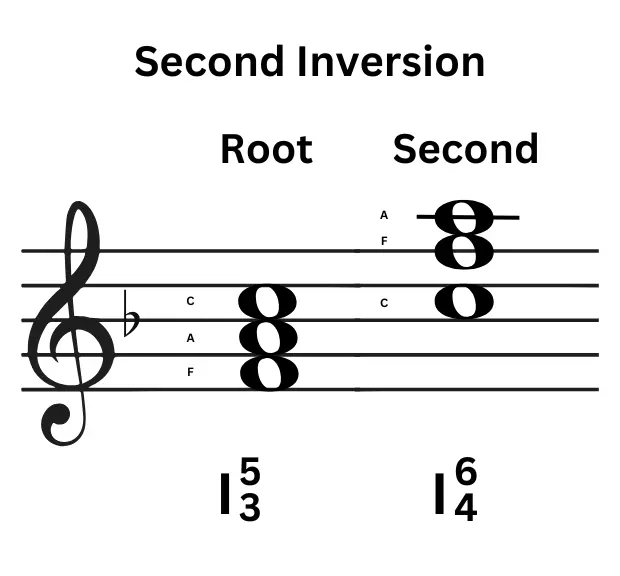
Second inversion of triads in music
It is evident that Triads definition music dictates that Triads are the 3 three notes stacked in ROOT + THIRD + FIFTH, in this position. Changing the position of the Third Note, that is, moving it to the bass or the root position gave us the First Inversion. Now, changing the position of the fifth Note, that is, moving it to the root position gives us the Second Inversion of a Triad.
For example,
a F major Triad structure is F-A-C.
A Quick Reminder!
It’s never too late to start learning! Book your free demos with us @ MUSICMASTER
How to use triads in jazz music?
So it gets more juicy here, stay with me! Triads are used in Jazz music to bring out some interesting harmonies. It’s not just that, these triads get expanded into some more complex chords like the sevenths, ninths etc. Jazz music uses the concepts of Triads for smooth transitions between chord progressions.
Secondly, Jazz is an epitome of improvisation and Jazz musicians often use the tones of Triad chords and Triad inversions such as tone of root, third or fifth while improvising their solos. This sums up the best resources to learn Triads in music theory
To learn more interesting concepts easily, book a Free Demo with Musicmaster today!
FAQs
What are Triads in music?
Triads in music refers to the 3 note chords used to build harmonic progressions in Music.
How do Triads work in Music?
Triads work as the basic harmonic units in Music.
What are the Different Types of Triads?
The Different types of Triads include Augmented, Diminished, Major and minor Triads.
What is the root of a Triad?
A root note has the lowest pitch of all the notes in triads and is known to be the bass note.
Where to find the best resources to learn Triads in music theory ?
Some of the Best resources to learn Triads in music theory can be found online.
How to learn Triads on guitar step by step ?
You can learn Triads on guitar step by step by watching video tutorials on youtube or by taking lessons from a professional.
What are the Triads Guitar chords for beginners ?
As a beginner, triad guitar chords can be practised with three fingers. For instance C major chords consist of C,E,G. So use one finger for each note. But certain triads are really tricky. To learn more, Book a free demo with us
Related Blog: Circle of fifths



























