Understanding music interval theory was pretty sweaty for me! Wink! Wink!. If you are also facing this same problem don’t worry this blog helps you find answers for obvious questions like music interval meaning and it’s types. Are intervals and Intervals in Music Theory Different? What are the easy ways to understand it? and so on.
As a bonus I have mentioned some music interval example for better understanding, let’s get moving on!

I don’t think in terms of intervals. I think in terms of tonal colour. I am trying to play through as many keys as possible – Woody Shaw.
Music Interval Meaning
Basically, the distance between any 2 notes written on music staff is Intervals . In other words, the difference in pitch between any sounds or notes in melody, or music in general, make up the intervals. Every piece of music that you listen to is contains various types of Intervals. Furthermore, understanding this can help you improve your sight reading techniques, Aural training. It is a vital concept when it comes to music composition or while writing music.
These music theories can be observed when they are written, played, or sung together, as in a chord, or one after the other, as in any melody. Now you understand the music interval meaning now let’s see different types of interval in music in detail.
What are the Music Intervals Types?
Intervals fall into different categories according to the order or the sequence they are in. They are in Linear, Horizontal, Vertical orders. Using the sounds they produce, we can differentiate intervals. In that way music intervals can be Harmonic and Melodic.
Some terms to remember:
Semitone: Semitones are the smallest music interval. It is the distance between any two closest notes in any chromatic scale. Another name for semitone is Half step.
Tone: In simplest words, two semitones put together equals a tone. Whole Step is the other name given to tone.
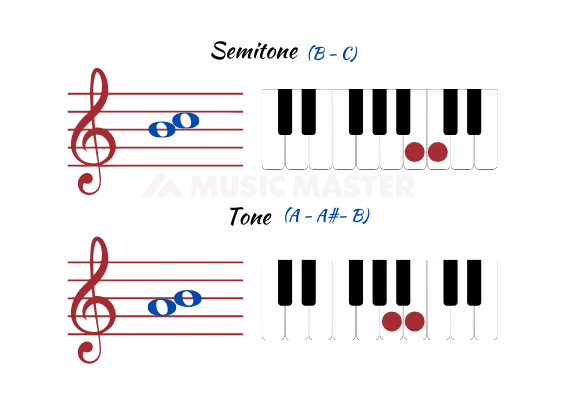

Did You Know?
We have Ditones which equals two whole notes or tones. Tritone in music is an interval that spans to 3 tones or whole steps.
Harmonic and Melodic Intervals In Music
Primarily, intervals can be of two types. Harmonic and Melodic. This can be grouped Based on different requirements.
Harmonic Intervals Explained
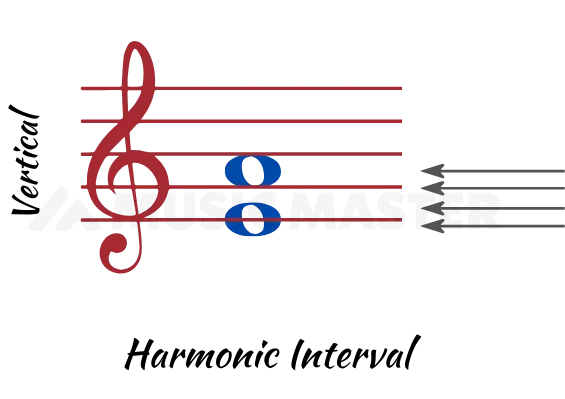
In a Harmonic interval, notes are played at the same time or simultaneously. A chord is an excellent example of Harmonic Interval or vertical interval.
Melodic Intervals Explained
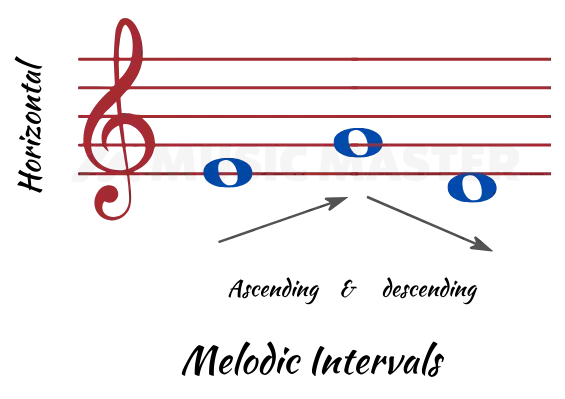
When you play notes one after the other or in a sequence, you create Melodic Intervals in music. Think of a broken chord or just any song. Melodic intervals can be in ascending or descending orders.
While we are here, let’s quickly look into Consonant and Dissonant Intervals. So, an interval is consonant if the notes sound peaceful or pleasant. An interval can be Dissonant if the notes sound tense and unpleasant
Types of Intervals in Music
Interval Numbers
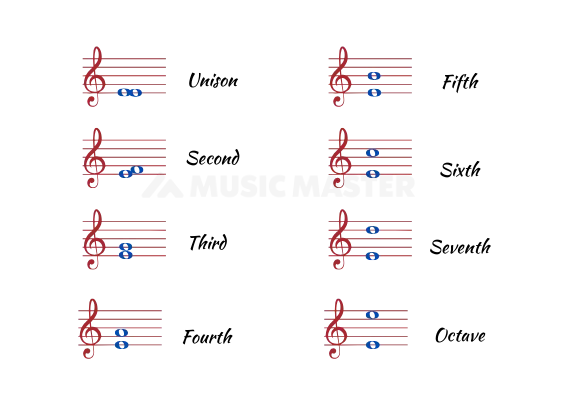
The word number here refers to the letter names of the notes on a musical staff. It stands for the numerical value allotted to a scale’s degrees. As long as you take the two notes that make up the interval from a diatonic scale, you can find the interval numbers by simply counting the degrees of the diatonic scale instead of looking at staff positions.
Here is an image of all the interval numbers to make understanding Intervals straight forward.
Interval Qualities
We have now seen that intervals are classified based on its numbers on a musical staff. Additionally, intervals are further classified on the basis of exact distance on a staff with a prefix added to interval numbers. The process of grouping intervals as Major, Minor, Perfect, Augmented or Diminished is called Interval Qualities.
Perfect Intervals
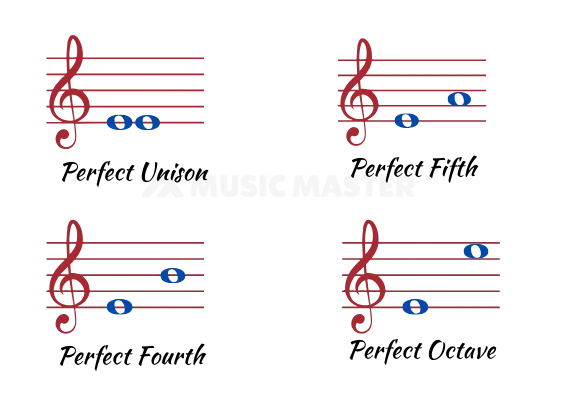
Perfect intervals in music are one of the essential. Here is the deal, only Unison, Fourth, Fifth and Octave are the Perfect intervals. In that way, the distance between any note and a Unison, Fourth, Fifth and Octave of the scale is known as Perfect.
Major and Minor Intervals
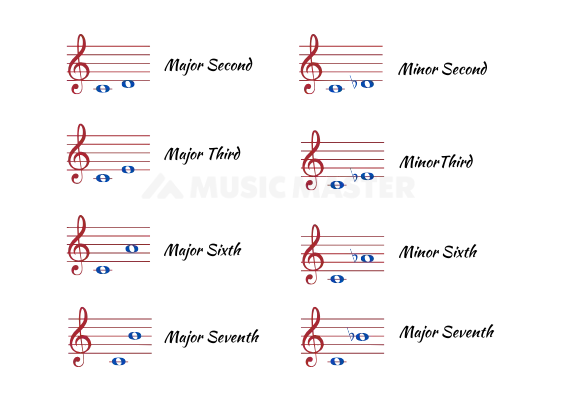
Just like Perfect intervals we have Major intervals in music. Major intervals are the intervals between the notes of a Major scale. As a rule, the second, third, sixth and seventh intervals can be referred to as major intervals. Basically , Major intervals are formed in a diatonic scale. Remember these terms tone and semitone?
Essentially, tones and semitones are the quickest way of finding major intervals in music, for example, C-E is a third interval. On a major scale a third interval will have a distance of 2 tones or 4 semitones. Therefore, E is 2 tones or 4 semitones away from C and so it is called a Major Third.
Now Let’s Discuss Minor Intervals
Now the easiest way of finding a minor interval is that it is one semitone lower than a major interval. We now know that C-E is a major third because it has two tones or four semitones. Now, let me pull the E a semitone lower to Eb. C-Eb would have three semitone distances and this would be called Minor Third.
Diminished and Augmented Intervals:
Semitone extended to a perfect interval is an Augmented Interval. C-F is a perfect fourth and adding a semitone to it, C-F# becomes an Augmented Fourth or a Diminished fifth with 6 semitones. Tritone is another name given for Augmented fourths as they have 3 tones.
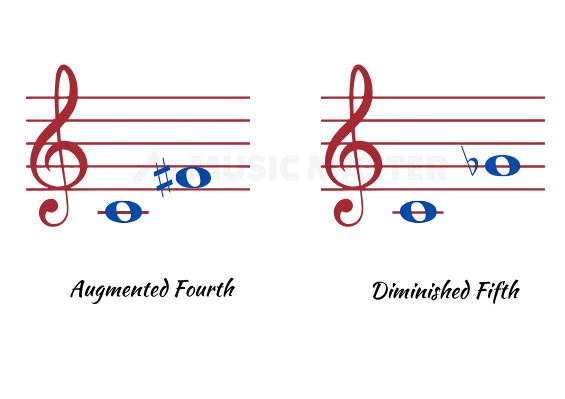
The gap of six half steps between the two intervals, which can be either a diminished fifth or an Augmented fourth.
So, here is a chart of all the music interval qualities that you need to know along with it’s names.

Interval Inversions
In simple words, an interval that has been inverted is one in which the higher or lower note is moved one octave up or down. This way, a new interval is produced when the existing interval is inverted.

Now it is very important that an interval’s total number of degrees plus its inversion always equals nine degrees. For instance in the image above C-G is an interval of Perfect Fifth. The original note C and that inverted here equals nine degrees.
Let us look at the usual inversions of intervals in Music. Generally, Perfect intervals always stay perfect; the quality of an inverted interval is the inverse of the original interval’s quality.
For instance,
- Starting with Unison. Unison when inverted becomes an interval of Octave.
- A perfect fourth inverted turn into perfect fifth;
- A second Interval when inverted becomes seventh;
- To arrive at Sixth, a Third is inverted.
This is like a formula to help you remember the inversions properly.
For instance, C-E is an interval of Major third. When the C is inverted an Octave up, the major third becomes a Minor Sixth (E-C).

Closing Thoughts!
Intervals in Music Theory happen to hold an important place while writing music. This is not a very complex concept. But like I always say, progressive learning requires guidance. Musicmaster will always be happy to guide you in the right path. Book a free music class demo Now! Happy Learning!
Just like the intervals, learning about notation and sight readings are also equally important.
FAQs
How do you define intervals in music?
Distance between any two notes written on a staff notation in music is called its interval.
What is the purpose of understanding intervals in music?
It can help you improve your sight reading techniques, Aural training. It is a vital concept when it comes to music composition or writing music.
Can you explain the difference between melodic and harmonic intervals?
When notes are played at the same time or simultaneously, it is called a Harmonic Interval wherein when notes are played one after the other or in a sequence, it is called Melodic Interval.
What are the different types of intervals in music?
Types of intervals in music include Harmonic and melodic based on characteristics, Perfect, major, minor, augmented, diminished based on qualities or size.
How do you name intervals in music?
Ideally, Intervals are named according to its degree numbers on a diatonic scale or position of notes on a musical staff.
What is the significance of perfect, major, and minor intervals?
The concept of exposing the intended emotion of musical piece is a significance of perfect, major, and minor intervals.