From ‘Ode to Joy’ to the catchy chorus of ‘Closer,’ melodies are the driving force. I would say melody music is arguably one of the most fundamental concepts. Every simple folk song or a complex classical piece is melody centric. That is probably why we could connect to these pieces emotionally and even remember them. All in all, melodies are the backbone of musical works.
Let’s look into ‘What is Melody?’. This article will also explore the characteristics of melody, concepts of melodic voice, Examples of melody in music, how it interacts with complex harmony, techniques used to craft it. We will also take a deeper dive into the essential elements of melody music.
What is Melody?
Well, technically it’s a series of musical notes played or sung or written one after the other to form a melodic structure or a tune. These notes are usually arranged in sequence and a rhythm pattern. This is the part of a song or any musical piece that a listener remembers most easily, often referred to as ‘tune.’ Does the melody meaning in music make sense now?

Did You Know?
The word ‘Melody’ meaning in Hindi, translates to ‘Sangeet,’ a rhythmic and harmonious sequence of musical notes.
The Anatomy of a Melody
There are a few elements that define melody.
Pitch
The changes in sound, high or low of the notes of melody in different music genres.
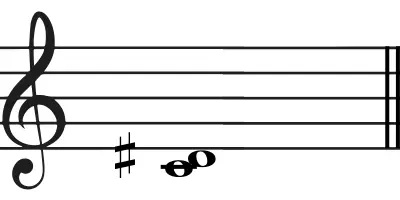
Rhythm
The pattern of silences and notes or even the duration notes in a melody.

Contour
The overall shape, ascending and descending motion in a melody.
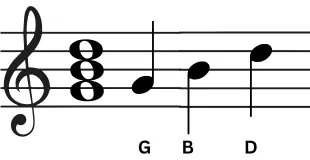
Harmony
The combination of notes played or sung simultaneously that support a melody.
So, Pitch vs harmony vs rhythms constitute melody in a Music composition. It is created with the intention of conveying emotions for the purpose of strong reactions in listeners.
Here is a A side-by-side comparison of these three concepts with examples for better understanding.
| PITCH | HARMONY | RHYTHM |
| Highness or lowness of a sound. | Combination of different notes or chords played simultaneously. | Pattern of silences and sounds |
| Pitch describes the frequency of a note in a melody. | Harmony complements melodies | Defines how long or short notes are held in a melody. |
| Eg: “Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star” – The melody starts with a relatively high pitch on “Twinkle” and moves down as the melody progresses. | Eg: Let It Be” by The Beatles – The melody is supported by the harmonic chords played on the piano, creating a rich texture throughout the song | Eg: “We Will Rock You” by Queen – The iconic stomp-clap rhythm is a clear example of how rhythm sets the pulse and creates anticipation. |
Melody in Music History
The words ‘melodious’ meaning in English, is a sweet sound that is pleasant to listen to.
Now, Evolution of melody in music is an interesting topic. I often enjoy reading about it. Here is a brief text about the role of Melody in music history and how each period contributed in the development of melody music.
In the days (before the 1600s), there were Gregorian Chants which hace monophonic melodies. That means single, unaccompanied melodic voice or line. These tunes are simple and repetitive.
Renaissance and Baroque (1400-1750s) saw multiple independent melodic lines played simultaneously, more like complex harmony. Like I have named it, this added more complexity to the musical pieces written.
The Classical period (1750-1820) had composers like Haydn, Mozart, Beethoven and others using clear and balanced melody music, with more complex harmony structures. Different melodies and musical phrases were characterised by something called symmetrical phrasing.
The Romantic Period’ (1820-1900) composers sought to use melody in classical music to express emotions and expressions.
In the Contemporary period (1900-present) definition of melody saw a development of challenging melodic lines. Composers like Stravinsky did not follow the traditional structures. More unconventional rhythms, dissonant sounds with new approaches to define melody.
Types of Melodies
Now, Melodies can be differentiated based on how one note moves to another. These movements can be smooth or with short or larger jumps between Intervals. These moves can be in ascending or descending orders, rising and falling in pitches. Let’s look into conjunct, disjunct, ascending, descending and static melodies with examples.
Conjunct Melodies
Notes that move by a step is the ‘Conjunct melody’ meaning in music. These melodies have small intervals between the consecutive notes. Typically, these movements are smooth and have a flowing sound. They’re also easy to follow.

Think of the melody of ‘Twinkle Twinkle, Little Star.’ Its notes have small intervals and is one of the easiest songs to sing.
Disjunct Melodies
Disjunct types of melodies have larger intervals between their notes. Larger leaps make it sound dramatic or irregular. Unlike conjunct melodies, these have jumps including thirds, fourths or even an octave.
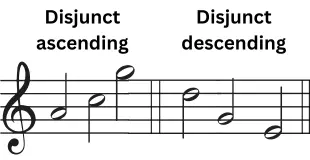
Example: the opening line of the song ‘Somewhere Over The Rainbow,’ has a jump with an interval of octave.
Ascending Melodies
As the name suggests, pitches increase as the melody progresses in ascending types of melodies. These melodies usually convey happy emotions like excitement and triumph.

For example, the popular ‘Do-Re-Mi’ from ‘The Sound of Music’ is an excellent example of ascending melodies
Descending Melodies
Descending melodies are the ones whose pitches decrease as the melody progresses. This means that the notes typically move lower in a scale. These melodies sound reflective or melancholic.

Have you heard of this English folk song called ‘Greensleeves?’ The Musical phrases in this song, structured with descending melodies, is an excellent example of this type of melody.
Static Melodies
Static melodies refers to the melodies with no change in the pitch. It stays on one note sustained for a long time. In general, these types of melodies are very less likely to be made because they sound monotonous. These sound emphasis stillness.

The opening of “Ode to Joy” has the ‘E’ being repeated and sustained. This could be static in nature.
Melody in Different Genres
So, what is a melody? And how complex harmony supports melody in different genres in music will be discussed below.
Melody in Classical Music
I am not going to lie, melodies in classical music are often complex and let’s not forget, highly structured. Composers also use complex harmony, themes and other variations to keep the melody music engaged.
Lets, for a minute look into the opening of Beethoven’ Symphony No.5. This iconic piece has elaborate melodies in different tempo, rhythm with counterpoints and motifs. It is the beautifully written melodies that contribute to a thematic development.
Melody in Pop Music
When it comes to pop music, catchy and memorable yet simple melodies are composed to appeal to the audience.
Listen to ‘Bye Bye Bye’ by ‘Nsync.’ The melody of the chorus is very repetitive, catchy and simple while the verses have variations. The sound of a symphony is leaps and bounds different from the sound of a pop song
Melody in Jazz Music
Jazz melodies are improvised and very spontaneous and free in nature. Musicians often experiment and explore harmonic possibilities. These melodies are generally syncopated with usage of blue notes (slightly flattened pitches).
Listening to ‘Take the A Train’ by Duke Ellignton, is an excellent example of swing melody with syncopated phrases. This melody also has fluctuating dynamics and a lot of room for improvisation.
Closing Thoughts
Melody shapes up any music. It is the most fundamental concept in music as well. To learn more concepts like this in a fun way, book a free demo with musicmaster, today!
FAQs
What makes a good melody?
A good melody is often memorable, engaging and appealing to the listeners.
Give ‘melody voice’ meaning?
‘Melody voice’ meaning is the primary lead voice that sings the main melody of a song.
Can a song exist without a melody?
No, a song cannot exist without a melody.
What are the elements of a melody?
Pitch, Harmony, Rhythms, Contour are the elements of a melody.
What is' Melody' meaning in hindi?
'Melody' meaning in Hindi translates to ‘Sangeet’ which means series of musical notes played or sung one after the other.
How can I get a melodic voice ?
Proper practice is the best way to get a melodic voice.
What is the difference between a melody and a tune?
Melody and tune are often interchangeable. A tune can be a simple melody, while melody is a series of notes played.
Give melodious meaning in english.
The word melodious meaning in English is used to describe pleasant, soft sounds in music
How do you define melody?
It's a series of musical notes played or sung or written one after the other to form a melodic structure or a tune.
What are the types of melody music ?
Melody music has conjunction, disjunct, ascending, descending and static melodies.
How to write a melody for a song?
To write a melody, begin with chord progression, set the groove with a catchy rhythm and set a pitch according to the theme.
What is the role of melody in music?
Melody shapes up music.
Where can I find melody songs audio ?
You can find melody songs audio on youtube or any audio streaming platforms.
Related Blog: Cadence in Music


































